We talk about ITSM principles as if they're separate from the actual work of managing services. They're not. Principles help you decide which ticket to prioritize when everything feels urgent, whether a change is worth the risk, or how much automation makes sense before losing the human touch. Organizations that anchor IT operations in clear principles see more consistent results because their teams make sound decisions even when situations don’t match the process documentation. That’s the real value: giving people a way to think through problems instead of relying on checklists alone.
TLDR:
ITSM principles guide IT decisions across incident response and change management.
AI-powered incident management cuts resolution time by 54% through smart routing.
Self-service portals reduce ticket volume when users find accurate answers quickly.
Slack-based ITSM removes friction by letting employees create tickets in chat.
Ravenna converts Slack messages into tickets and uses AI to answer routine questions.
Core ITSM Principles That Drive IT Excellence
ITSM principles are the fundamental guidelines that shape how IT teams deliver value through effective IT service management. They act as guardrails that keep service delivery aligned with business goals and evolving business needs, even as priorities shift or new challenges emerge. These principles go beyond specific frameworks or tools, providing a consistent approach to decisions around incident response, change management, and service improvement.
Principles differ from processes in a critical way. Processes define what to do in specific scenarios, while principles guide how to think when making any ITSM decision within an ITSM framework. They help teams weigh trade-offs, assess competing demands, and maintain service quality without rigid rules that fail in real-world situations.
Organizations that anchor their IT operations in clear principles see more consistent outcomes. When your team understands the underlying philosophy behind service management, they can adapt workflows to fit your unique environment instead of forcing your business into a template. This flexibility becomes critical as you scale or integrate new services.
Strong ITSM principles also create a shared language across IT and business stakeholders. When everyone agrees that services should focus on user value or that continual improvement matters, decisions become less contentious and alignment happens faster.
ITIL 4's Seven Guiding Principles for ITSM Success
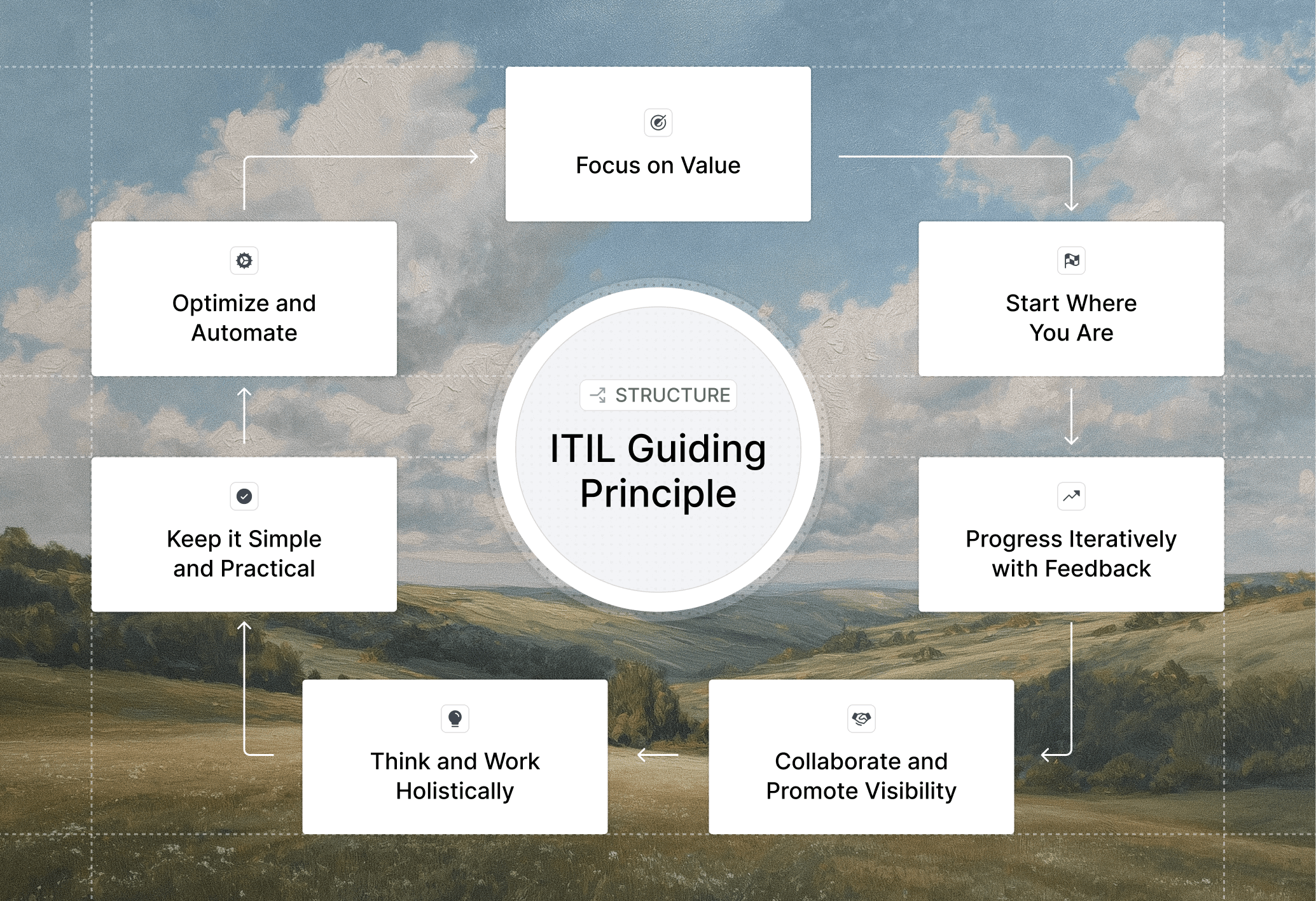
ITIL 4, part of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, defines seven guiding principles that apply across every ITSM decision, from daily ticket triage to multi-year transformation initiatives. These principles work together as a decision-making framework instead of isolated rules.
Focus on Value
Every service activity should tie back to outcomes that matter to users and the business. When assessing any change or new process, ask whether it delivers value or just adds overhead.
Start Where You Are
Assess your current state before designing new workflows. Most organizations already have useful processes, tools, and knowledge that can be built upon instead of replacing wholesale.
Progress Iteratively with Feedback
Break large improvements into smaller cycles that you can test and refine. Collect feedback from users and support teams after each iteration to guide the next step.
Collaborate and Promote Visibility
Service delivery requires input from multiple teams and stakeholders. Make work visible across groups so everyone understands dependencies, priorities, and how their contribution fits into broader goals.
Think and Work Holistically
ITSM decisions ripple across the organization. Consider how incident response affects change management, how knowledge creation impacts self-service adoption, and how automation touches multiple workflows simultaneously.
Keep It Simple and Practical
Eliminate unnecessary complexity in processes and tools. If a workflow requires ten approvals or a form has thirty fields, you are likely creating friction that slows resolution without adding real control.
Optimize and Automate
Look for repetitive tasks that drain team capacity and automate them where it makes sense. Optimization should happen continuously as you gather data on what actually works versus what sounded good in theory.
Putting the Principles Into Practice
While those ITIL guiding principles form the foundation of successful IT service management, ITSM processes are the mechanisms through which those principles are enacted. We have identified several key processes that every IT organization should assess against those principles:
Incident management
Change management
Knowledge management
Self-service
Incident Management Principles for Faster Resolution
Incident management focuses on restoring normal service quickly while minimizing business impact across the service desk and support teams. Detection must happen before users notice problems, with automated monitoring catching issues early and giving teams time to respond.
The key is proper categorization. This routes incidents to the right team with accurate priority levels, preventing delays and ensuring urgent issues receive immediate attention. Categorization also reveals patterns that point to underlying problems. Resolution must balance speed with quality, aiming to resolve issues permanently rather than simply closing tickets. Organizations using AI in incident management have seen a 54% reduction in resolution time through intelligent routing and automated responses.
At the heart of incident management are structured workflows which create the consistency needed for an effective process. When teams follow the same escalation paths, communication protocols, and documentation standards, resolution becomes predictable and incident data easier to analyze for prevention opportunities.
Change Management and Controlled Service Updates
Change management controls how updates move through your IT environment without causing outages, security gaps, or unnecessary disruptions. Every change should undergo assessment for risk, business impact, and rollback options before touching production systems. This is helped by using structured approval workflows, which match stakeholder review to change scope and risk level. Standard changes with proven track records can follow expedited paths, while high-risk updates require broader review.
When understanding the impact of change, it's all about answering three questions:
What could break?
Who will be affected?
How do we revert if something goes wrong?
Organizations with mature change management experience fewer incidents because they catch conflicts and dependencies before deployment. And, those same organizations understand that tracking change outcomes reveals patterns, which inform better decision-making and help teams refine processes over time.
Knowledge Management as a Service Delivery Accelerator
Knowledge management turns resolved issues into reusable assets that speed up future service delivery. The Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS) methodology treats documentation as a living resource created during problem resolution instead of as a separate writing task. When support agents capture solutions while they work, knowledge stays current and reflects real user questions. Each resolved ticket becomes an opportunity to strengthen your knowledge base without dedicated authoring time.
But just capturing solutions isn't enough. To truly make knowledge management impactful, you'll need structure, which makes information findable when needed. Articles should answer specific questions with clear steps, avoiding vague guidance. Tagging and categorization help users find relevant content quickly.
Teams with strong knowledge bases resolve incidents faster because agents find proven solutions instead of troubleshooting from scratch. Self-service adoption increases when users can answer their own questions, reducing ticket volume and freeing support capacity for complex issues requiring human expertise. However, knowledge management content can become stale over time. Regular reviews help identify outdated articles, documentation gaps, and opportunities to consolidate redundant content.
Self-Service and Empowering End Users
Self-service moves routine problem-solving and common service requests from support agents to end users through accessible knowledge bases and intuitive interfaces, and tracking the right KPIs for employee self-service helps you measure adoption and impact. 73% of survey respondents consider self-service adoption a key initiative to mitigate resource constraints. But, effective self-service requires content that matches how users search for help, using plain language instead of technical jargon. Search functionality should surface relevant articles quickly, and navigation should feel intuitive to people unfamiliar with IT terminology. And if you want to accelerate self-service within your organization, you'll need to build trust between employees and the self-service tools. Users will only rely on self-service if they consistently find accurate, complete answers that improve the overall user experience.
Measuring ITSM Success Through Key Metrics
The true impact of an ITSM strategy is measurable through KPIs. For example, Mean-Time-to-Resolution (MTTR) tracks how long issues take to fix, revealing bottlenecks in workflows or knowledge gaps while First-Contact-Resolution (FCR) measures whether agents solve problems immediately or require multiple interactions. When you begin to measure your ITSM against those KPIs, you can develop SLAs to help build that trust, demonstrating whether teams meet promised response and resolution times. Organizations handle an average of 10,675 tickets monthly, with each user contacting the help desk 1.25 times per month. Finally, success is reflected through Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores that capture user sentiment and overall customer experience, identifying where service falls short despite meeting technical SLAs. Track these metrics over time to spot trends and support continual service improvement across your ITSM strategy.
Automating ITSM Workflows for Efficiency
IT workflow automation tools work best for repetitive tasks with clear triggers and consistent outcomes. A few simple examples, which follow predictable rules that rarely need nuanced decisions include:
Ticket routing based on keywords or category
Status updates when conditions are met
Acknowledgement messages
But not all tickets can be solved through automation. There will always be tickets that can't be solved with self-serve options. These tickets require escalation workflows, which can benefit from partial automation. Systems can flag tickets approaching SLA deadlines or meeting specific criteria, but human review of context before escalating prevents unnecessary escalations that frustrate teams.
When implementing automation workflows, AI-powered automation handles answering common questions from knowledge bases or suggesting solutions based on ticket content, reducing repetitive inquiries while maintaining answer quality through referencing verified documentation. You should reserve human intervention for situations requiring empathy, complex troubleshooting, or decisions with business impact. Automation is intended to expand your team's capacity to handle exceptions and provide personalized support when users need it most.
Integrating ITSM with Communication Tools
Traditional ITSM tools force users to leave their workflow, log into separate portals, and work through unfamiliar interfaces just to report an issue. This friction creates delays and discourages adoption, particularly for non-technical employees who avoid opening tickets until problems escalate.
Embedding ITSM directly into collaboration tools like Slack removes this barrier. When employees can create tickets, check status, and get answers within the chat environment they already use daily, support becomes frictionless. Conversational ticketing captures context naturally from message threads instead of forcing users to fill out forms.
Integration speeds resolution by keeping conversations in one place. Support agents see the full discussion history without switching between Slack and a separate helpdesk system, reducing back-and-forth clarification requests. This approach increases ITSM adoption because users receive help where they naturally ask for it.
Implementing ITSM Principles in Your Organization
So, how do you begin implementing ITSM principles into your organization?
First, start by documenting your current ITSM state before building new processes. Identify which workflows cause the most friction and where users abandon existing systems. This assessment reveals quick wins that show value early.
Next, choose a pilot team facing clear pain points instead of rolling out organization-wide changes. Test your ITSM approach with one department, gather feedback, and refine based on real usage patterns. Pilot success builds credibility with skeptical stakeholders.
Then, align improvements with specific business objectives that leadership cares about. Reducing resolution time matters more when framed as improving employee productivity instead of just an IT metric.
Finally, scale gradually by expanding to teams with similar needs first. Document what worked in your pilot and adapt those practices for each new group instead of forcing identical workflows everywhere.
Final Thoughts on Implementing ITSM Principles
Your IT team already handles complex problems every day, and ITSM principles give you a clearer framework for those decisions. Focus on principles that deal with your biggest pain points first, whether that's incident resolution speed, change management risk, or self-service adoption. Progress happens through small iterations, not massive overhauls.
FAQ
What are ITSM principles and why are they important for IT teams?
ITSM principles are guiding philosophies that shape how IT teams make decisions across incident management, change management, and service delivery. Unlike rigid ITSM processes, principles help teams prioritize work, manage risk, and align IT service management with business goals, even when situations don’t fit documented workflows. Strong ITSM principles improve consistency, decision-making, and service quality as organizations scale.
How do ITIL 4 guiding principles improve IT service management?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles provide a flexible framework for improving IT service management by focusing on value, collaboration, continual improvement, and simplicity. These principles help IT teams adapt their ITSM practices to real-world conditions instead of forcing strict processes. When applied correctly, ITIL 4 principles improve incident resolution times, reduce change-related disruptions, and strengthen alignment between IT operations and business objectives.
What’s the difference between ITSM principles and ITSM processes?
ITSM principles guide how to think, while ITSM processes define what to do. Processes outline steps for tasks like incident resolution or change approvals, but principles help teams make sound decisions when conditions change or exceptions arise. This distinction is critical for modern IT environments where rigid workflows often fail, and teams must balance speed, risk management, and user experience.
How can ITSM principles reduce incident resolution time?
ITSM principles improve incident management by emphasizing early detection, proper categorization, and continuous optimization. When teams apply principles like “progress iteratively” and “optimize and automate,” they can use AI-powered routing, structured workflows, and knowledge management to resolve incidents faster. Organizations adopting AI-driven ITSM have reduced resolution times by eliminating manual triage and repetitive tasks.
When should IT teams automate ITSM workflows?
IT teams should automate ITSM workflows when tasks are repetitive, predictable, and rules-based, such as ticket routing, status updates, and common service requests. ITSM principles help teams decide where automation improves efficiency without harming service quality. Complex issues, high-risk changes, or situations requiring empathy should remain human-led to protect customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
Why is self-service a core principle of modern IT service management?
Self-service is central to modern ITSM because it reduces ticket volume, improves user satisfaction, and scales IT support without increasing headcount. ITSM principles encourage building intuitive self-service portals backed by accurate knowledge bases so end users can resolve issues independently. It plays a direct role in improving service delivery and operational efficiency.




