Your helpdesk queue is full of tickets that don't need a human to solve them for your end-users. Service desk automation uses AI to handle password resets, access requests, and common questions automatically while routing everything else to the right person immediately. In modern IT service management (ITSM), the global helpdesk automation market is hitting $8.14 billion in 2025 because companies are tired of paying agents to do work that software can handle better. Twenty-two percent of all support tickets now resolve without human involvement, turning automation into a clear source of cost savings, and that number keeps climbing.
TLDR:
Service desk automation deflects 35% of tickets through AI-powered self-service portals.
Conversational ticketing in Slack eliminates portal switching and speeds resolution.
Automated workflows handle access requests, approvals, and provisioning without manual steps.
AI classification routes tickets to the right resolver instantly based on request content.
Ravenna delivers Slack-native ticketing with AI categorization and knowledge capture.
What Service Desk Automation Is and Why It Matters
Service desk automation turns your IT service desk into an automated service desk that uses AI, workflows, and self-service tools to handle IT support tasks without requiring manual intervention. Instead of agents manually sorting tickets, resetting passwords, or answering routine questions, automated systems take over these repetitive processes. The result is faster resolution times, lower costs, and more consistent service delivery for employees who get help when they need it.
The business case is clear. The global helpdesk automation market is projected to reach $8.14 billion in 2025 and grow to $24.93 billion by 2029 with a compound annual growth rate of 32.3 percent. Twenty-two percent of all support tickets are now resolved without human involvement. That means roughly one in five requests never reaches an agent's queue, reinforcing automation as a core part of modern IT service management strategies.
Service desk automation works across three core areas:
AI handles intelligent routing and classification, learning from past tickets to predict the right category and owner.
Workflows connect triggers to actions, so creating a ticket can automatically provision access or send approvals.
Self-service portals let employees find answers in knowledge base articles and submit service requests without opening a conversation with support.
The 15 strategies below show you how to implement automation tools across your service desk, from ticket classification to predictive analytics. Each strategy targets a specific pain point and helps you streamline a scalable support operation without adding headcount.
AI-Powered Ticket Classification and Intelligent Routing
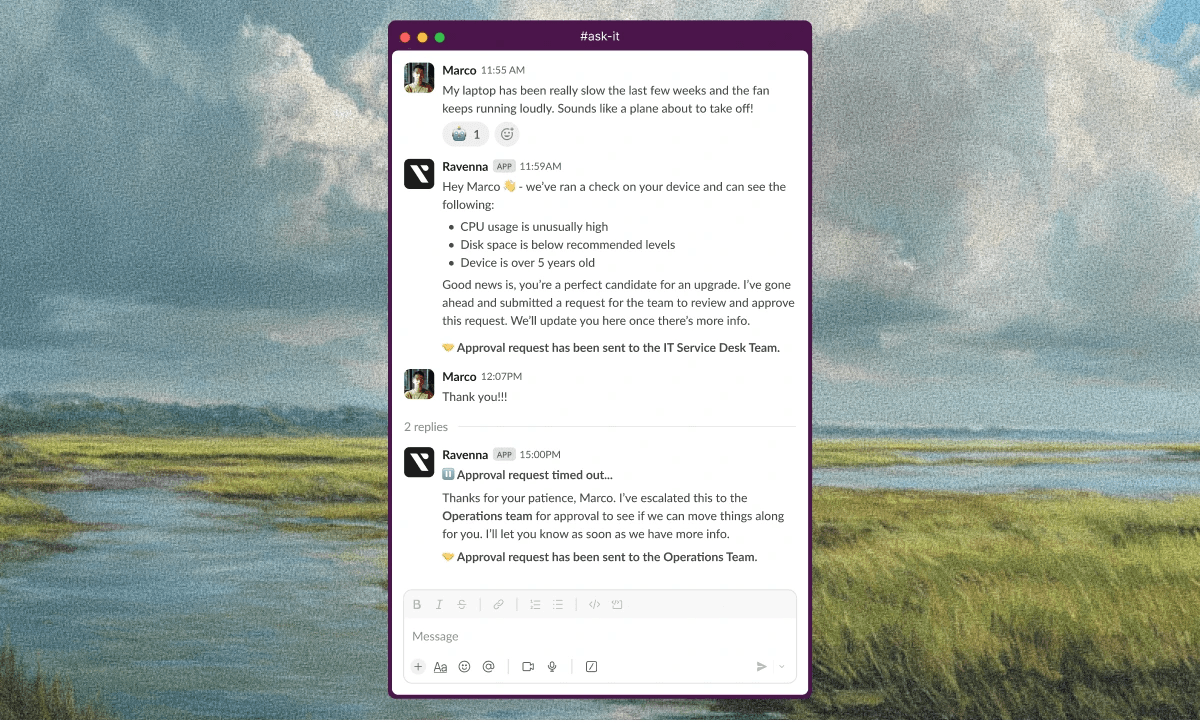
Manual ticket triage burns hours each week. An agent reads every request, categorizes it by guesswork, and assigns it to someone who might have the answer. AI-powered classification cuts through that bottleneck by analyzing the language in each ticket and instantly determining type, priority, and ownership.
The system learns from historical data to spot patterns. A request mentioning "can't access Salesforce" gets tagged as an access issue and sent to identity management. A message about "laptop overheating" goes to hardware support. Accuracy improves with each processed ticket as the model refines its understanding.
Intelligent routing then delivers tickets to the right resolver immediately. Requests land with subject matter experts who can close them fast instead of bouncing between teams or waiting in a general queue. First-contact resolution rates climb while reassignments drop.
Service desk automation that includes automatic classification reads incoming messages, identifies intent, sets priority, and triggers the matching workflow without dropdown menus or intake forms. Resolution speed increases, analytics improve, and support staff solve problems instead of sorting them.
Conversational Ticketing Through Collaboration Tools

Conversational ticketing in Slack lets employees create support requests directly instead of navigating to separate portals. They describe issues in a message, add an emoji, or use a slash command. The ticketing system converts that input into a tracked ticket without redirecting them elsewhere while updates and resolutions appear in the same thread where the request started.
This removes context switching. Teams stay focused without jumping between apps to check ticket status or add details and support staff respond within the collaboration tool itself, treating requests as threaded conversations, not isolated queue items. The result is that adoption rates increase because the friction of requesting help disappears and the employee experience improves. When creating a ticket feels like messaging a colleague, end-users stop attempting to solve problems alone or delaying until issues escalate. Service desk automation built into these tools meets people where they already work.
Self-Service Portals and Knowledge Base Automation
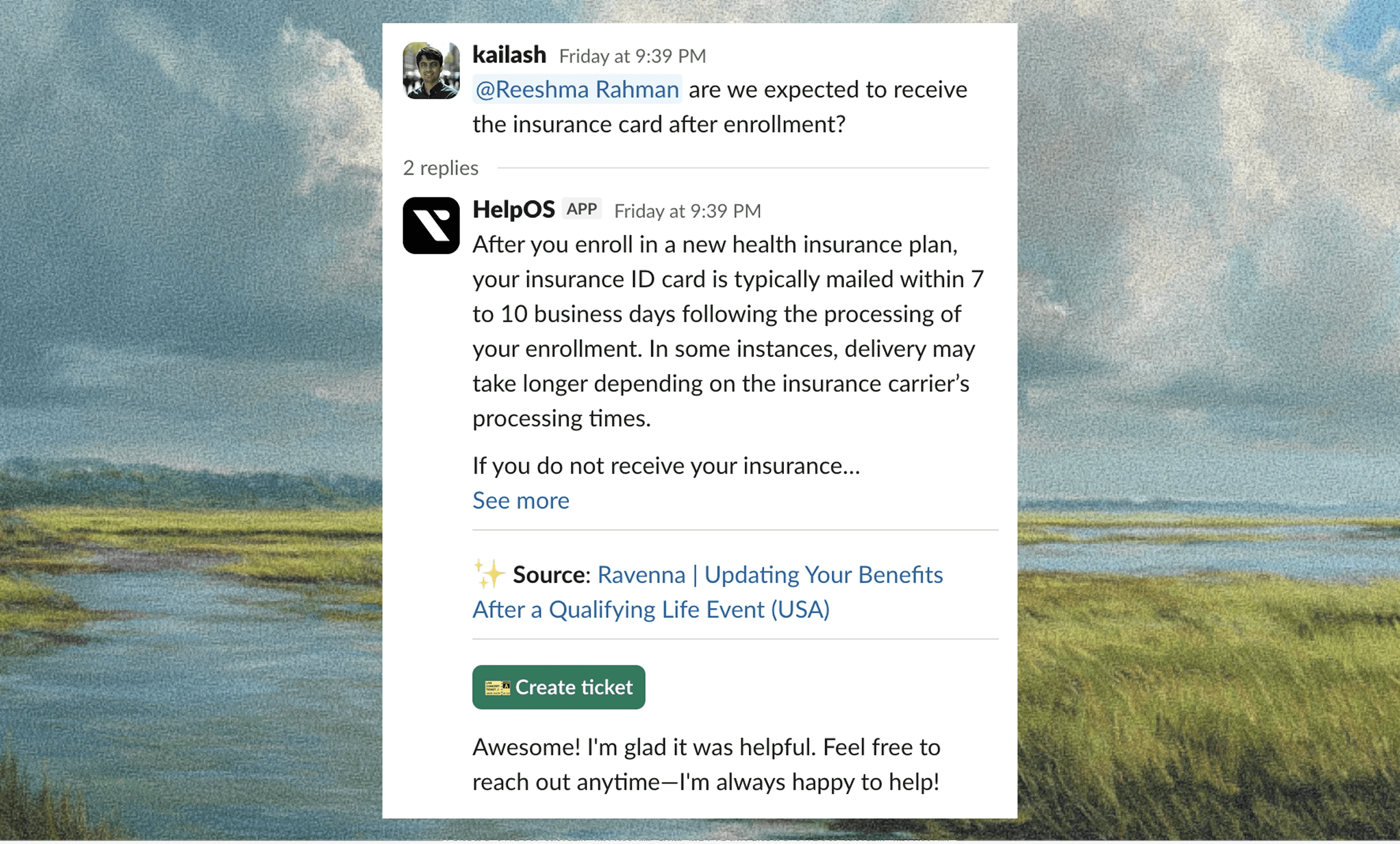
Self-service portals cut ticket volume by letting employees find answers (self-service) without agent intervention. And this has been proven as AI-driven self-service tools deflect 11% to 30% of incoming support tickets.
How does it work? AI-powered search interprets the intent behind questions and surfaces relevant articles from connected knowledge sources. Employees type queries in plain language and receive instant recommendations. Automated knowledge capture then converts resolved tickets into searchable articles automatically. When an agent solves a new issue, the system turns that resolution into documentation for the next person with the same question. This builds a knowledge base that grows with actual support interactions instead of relying on manual article creation.
The best part of this is that intelligent recommendations appear before employees submit requests. As someone begins typing a question, the system suggests articles that match their intent. If answers satisfy the need, a ticket never enters the queue.
Finally, portals that connect with Slack, Notion, Confluence, and Google Drive pull knowledge from where it already exists and surface it when needed. Seventy-three percent of survey respondents consider self-service adoption a key initiative to mitigate resource constraints.
Automated Onboarding and Offboarding Workflows
Onboarding and offboarding workflows remove manual provisioning tasks from IT teams. When an employee joins, workflows automatically trigger account creation, access provisioning, and credential delivery across connected systems from a single request. New hires receive software access and materials without agents coordinating between tools.
Offboarding works the same way. When someone leaves, workflows revoke permissions, disable accounts, and initiate asset recovery. Access gets terminated immediately instead of remaining active while agents manually work through deprovisioning steps, closing security gaps faster.
Integration with identity providers like Okta or Google Workspace links workflows to your directory. Adding a new hire to a role-based group can trigger automatic app access provisioning. Workflows handle approvals and notifications in the background while employees experience smooth transitions.
Smart Escalation and SLA Management
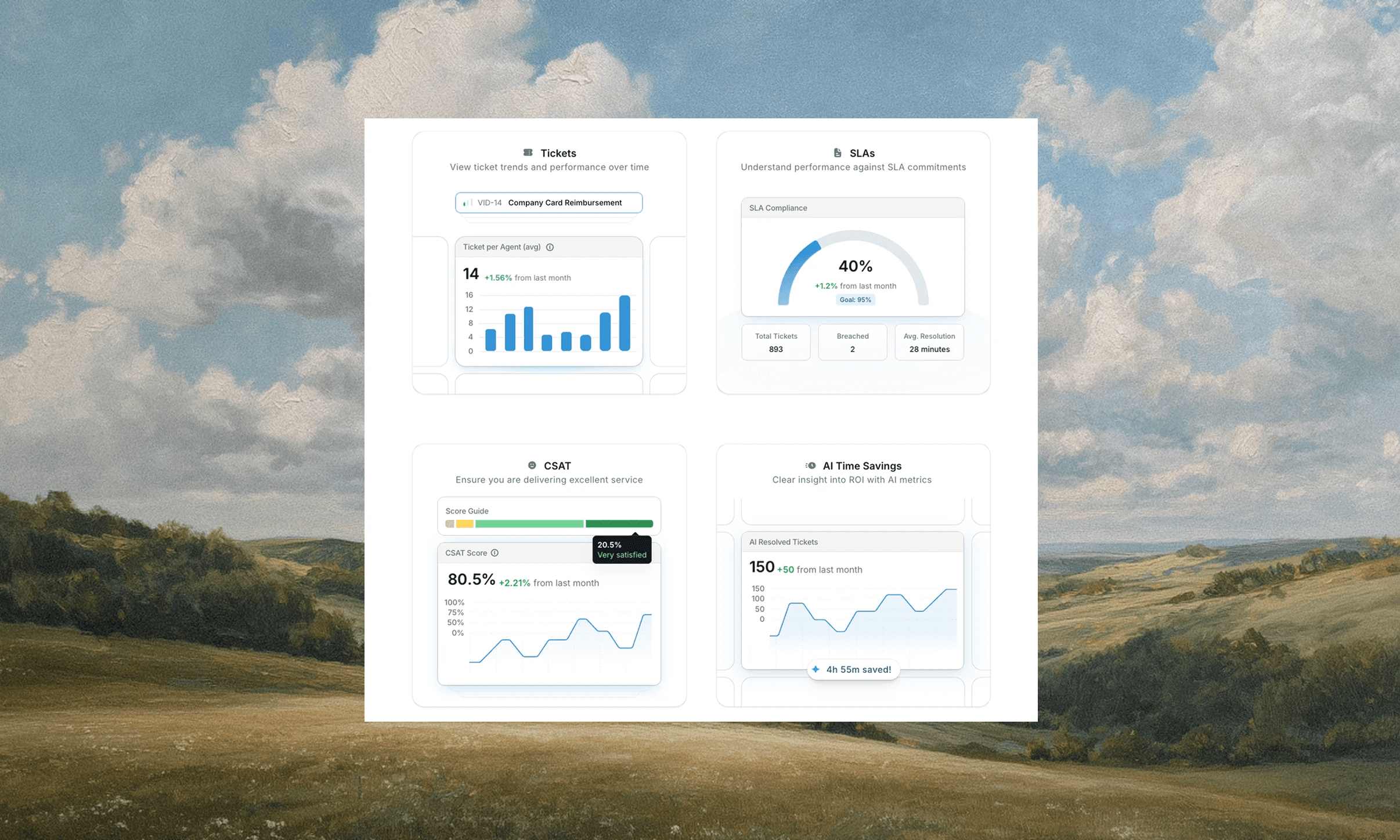
Automated escalation monitors ticket age, priority, and response times to prevent service level agreement (SLA) breaches before they occur. When a high-priority request approaches its deadline without assignment or resolution, the system routes it to the next tier or alerts managers for immediate action.
How does routing work? That's accomplished through business rules that take into account agent workload, expertise, and availability. Here's a real-world example: a critical database outage reaches your database specialist if they're available instead of queuing behind routine requests. This prevents senior staff from handling issues that don't match their skillset, while time-sensitive problems go unresolved.
SLA tracking dashboards surface breach rates, average response times, and pending escalations across teams and ticket types. Automated alerts notify stakeholders when tickets risk missing commitments, creating intervention opportunities before customers experience delays.
Automated Response Templates and Chatbot Deflection
Chatbots deflect tickets by answering common questions before they reach agents. Conversational AI interprets requests, searches connected knowledge sources, and delivers contextual responses instantly. Employees ask questions in a Slack DM or chat interface and receive answers drawn from documentation without waiting in a queue. When the bot can't answer, it escalates by creating a ticket automatically.
Workflow Automation for Access Requests and Approvals
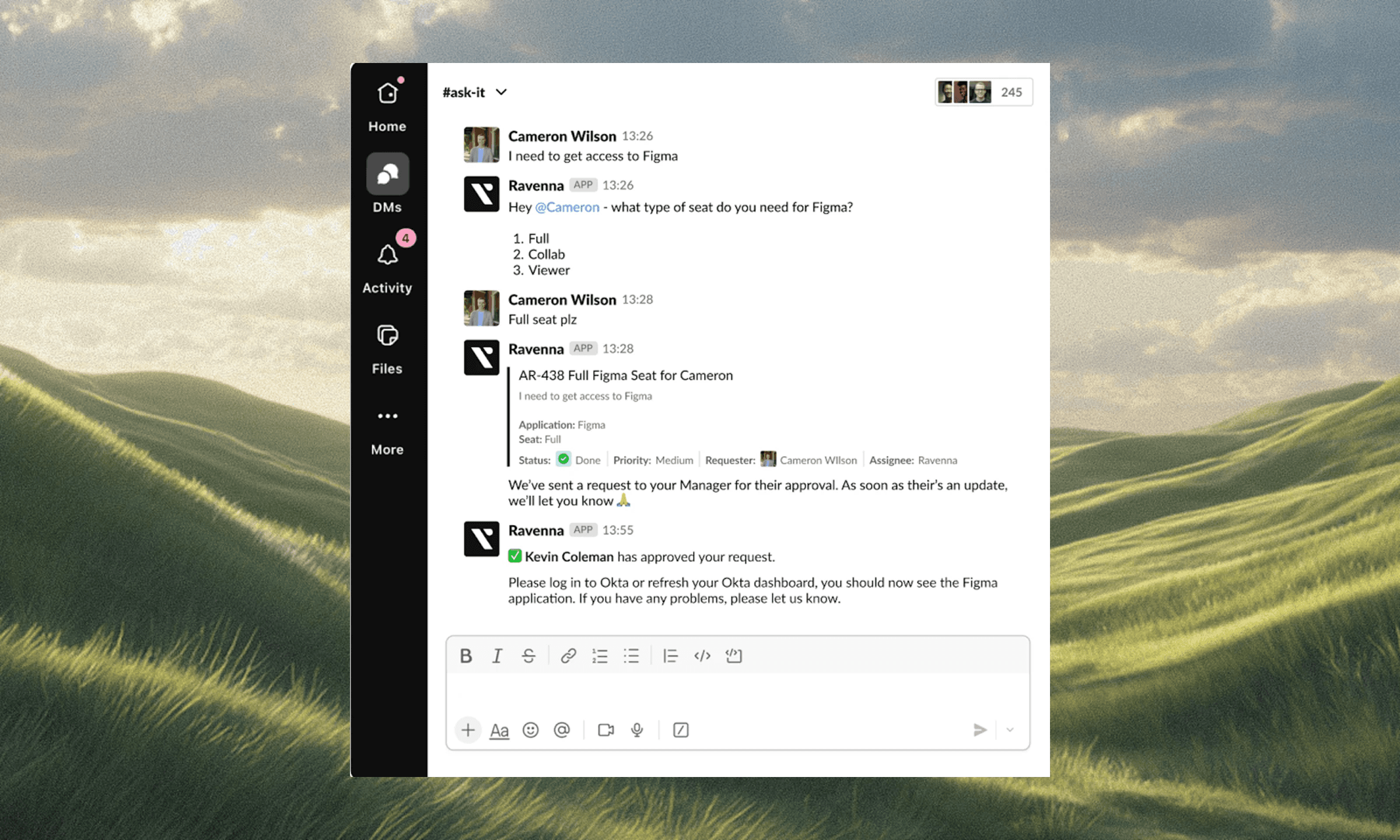
Approval workflows replace email chains and spreadsheet tracking with automated routing. When someone requests software access or hardware, the system identifies the required approver based on role, cost threshold, or department policy. The request moves to that person's queue with all context attached, and reminders fire automatically if approvals sit idle.
Multi-step approvals chain together without manual coordination. For example, a laptop purchase request might need manager approval followed by the finance review. Once the first approver acts, the workflow advances to the next step and notifies the second approver. Each decision gets logged, creating an audit trail without agents chasing signatures.
Finally, approved requests trigger provisioning immediately. Integration with identity providers like Okta grants access the moment approval comes through, which means the requester receives confirmation in the same thread where they submitted the original ask, and the ticket closes automatically once provisioning completes.
Predictive Analytics and Proactive Issue Resolution
Predictive analytics identifies problems before users submit tickets by analyzing historical data, system logs, and performance metrics. When identical errors appear across multiple devices or ticket volume increases for a specific application, the system flags these patterns for investigation.
Automated alerts give IT teams time to fix root causes instead of tackling symptoms. A recurring password reset issue or repeated software crash becomes an opportunity to correct the underlying configuration or deploy a system-wide patch, stopping tickets before they arrive.
Analytics dashboards reveal patterns across ticket types, affected assets, and failure points:
Application analysis showing which tools generate the highest request volumes
Team-specific data showing where repeated issues cluster
Documentation gap identification, revealing where self-service resources fall short
These insights inform decisions about infrastructure updates, process changes, and knowledge base expansion.
Automated Reporting and Performance Analytics
Automated reporting pulls metrics directly from tickets, workflows, and user interactions, eliminating manual data collection so you can optimize decisions with current data. Dashboards update in real time to display current ticket volume, open queue depth, and active SLA breaches while scheduled reports deliver weekly or monthly summaries to leadership without requiring analysts to compile spreadsheets.
The most important metrics include:
Resolution time
First-contact resolution rate
Average response time
Ticket volume by category
Agent workload distribution
These numbers quantify service desk performance and reveal where bottlenecks form or resources stretch thin.
Leadership uses this data to explain budgets, assess staffing needs, and measure the impact of automation initiatives. When a dashboard shows deflection rates climbing or average handle time dropping after implementing self-service, the ROI becomes visible. Automated alerts notify stakeholders when metrics fall outside acceptable ranges, prompting corrective action before problems surface in quarterly reviews.
Integration Automation Across IT Tools
Integration automation connects service desk systems with identity providers, issue trackers, and knowledge repositories through APIs. When someone submits an access request in Slack, the system pulls user data from Okta, checks approval policies, updates Jira for tracking, and provisions access automatically once approved.
What makes this so powerful is that data flows between tools without manual re-entry:
Identity changes in Google Workspace sync to your ticketing system
Asset records update across platforms when tickets close.
This prevents version conflicts and keeps employee information consistent wherever it appears.
Pre-built connectors link systems like Okta, Jira, Linear, Confluence, and Notion. These integrations turn isolated tools into a unified support operation where actions in one system trigger updates across the rest.
Automated Notification and Communication
Automated notifications remove manual status updates from your support team’s workloads. Requesters receive instant confirmation when they submit a ticket, including a reference number and response timeline. The system sends updates as tickets progress:
Assignment confirmations when an agent claims the work.
Status changes as resolution advances.
Closure notifications when issues are resolved.
Consistent communication improves user satisfaction and overall customer satisfaction with the service desk.
Automatic progress updates reduce status inquiry tickets. When resolution extends beyond initial estimates, the system notifies requesters with delay explanations and adjusted timelines. Escalation alerts flag tickets approaching SLA breaches, giving managers visibility into requests requiring intervention.
Finally, post-resolution satisfaction surveys deploy automatically, capturing feedback while experiences remain fresh. Response data flows into analytics dashboards that track service quality trends across request categories and support teams.
Password Reset and Account Management Automation
Password resets and account unlocks consume disproportionate agent time relative to their technical complexity. Employees forget credentials, lock themselves out after failed login attempts, or need profile changes that require manual verification. These requests clog queues despite following identical resolution paths every time.
Self-service password reset automation lets employees verify identity through multi-factor authentication, security questions, or email confirmation, then reset credentials immediately. Account unlock workflows follow the same pattern, checking identity and restoring access without agent involvement. Profile updates for phone numbers, department changes, or manager assignments flow through automated approval chains when policy requires sign-off or complete instantly when verification passes.
Integration with identity providers like Okta or Google Workspace executes changes across every connected system simultaneously. One password reset updates access everywhere instead of requiring agents to touch multiple tools.
Automated Software Deployment and Patch Management
Automated software deployment distributes applications and updates across devices without manual installation. Scheduled deployments push patches during off-hours to avoid disrupting work, while silent installs complete in the background as employees continue using their machines.
Prior to distributing updates, automated testing validates patches in staging environments before production rollout. When updates cause conflicts or performance issues, rollback capabilities revert systems to previous stable states automatically (in the event a rollout was initiated with an unforeseen impact), preventing widespread failures across your fleet.
Compliance requirements stay current as automation tracks installed software versions and flags devices running outdated or vulnerable applications. Security patches deploy immediately upon release, and audit logs document every deployment for compliance evidence without manual tracking.
Measuring Automation ROI and Continuous Improvement
Help desk automation can sometimes save upwards of 25 percent of agents' time on repetitive tasks, depending on the ticket type. These hours convert directly to cost savings, better service delivery, or capacity for higher-value work. But, how do you know if service desk automation is having the impact you expect it to have on ticket resolution? That can be understood through measurement.
Start with three core metrics to calculate automation ROI:
Ticket deflection rate
Average handle time reduction
Cost per ticket
Track how many requests self-service resolves before reaching agents, measure time saved on automated tasks, and multiply deflection volume by your cost per ticket to quantify savings. Continuous improvement, though, requires monitoring what automation misses. Review escalated tickets, low-confidence classifications, and repeated manual interventions to identify where workflows need refinement or knowledge bases require expansion.
Final Thoughts on Implementing Service Desk Automation
Service desk automation gives your IT team breathing room by handling the tickets that follow the same pattern every time. You don't need to automate everything at once. Start with self-service password resets or intelligent ticket routing, track the time you save, and add more workflows as your confidence grows.
FAQs
How do I start implementing service desk automation without disrupting current operations?
Begin with high-volume, low-complexity tasks like password resets and ticket classification. Deploy self-service options for common requests first, then layer in intelligent routing and workflow automation as your team adapts to the new system.
What's the difference between chatbot deflection and self-service portals?
Chatbots provide conversational AI that answers questions in real-time through chat interfaces, while self-service portals offer searchable knowledge bases where employees browse articles. Both reduce ticket volume, but chatbots interpret natural language requests and portals require employees to search for solutions.
When should I consider moving from manual ticket triage to AI-powered classification?
If your team spends more than 5 hours per week categorizing and routing tickets manually, or if misrouted tickets cause delays in resolution, AI classification will deliver immediate time savings and accuracy improvements.
Can service desk automation integrate with our existing identity provider and knowledge tools?
Yes, modern automation platforms connect with identity systems like Okta and Google Workspace, plus knowledge sources including Confluence, Notion, and Google Drive through pre-built integrations that sync data automatically without custom development.
Why does automated escalation matter if we already have SLA tracking?
SLA tracking shows when breaches occur after the fact, while automated escalation prevents them by routing at-risk tickets to available resolvers before deadlines pass. This proactive approach maintains service commitments instead of documenting failures.




